Can Exercise Improve Your Eye Health?

When it comes to maintaining optimal health, exercise is often at the forefront of discussions. While physical activity is well-known for its benefits to cardiovascular health, mental well-being, and overall fitness, its impact on eye health is sometimes overlooked. However, there is growing evidence to suggest that regular exercise can indeed contribute to better vision and protect against age-related eye conditions. In this article, we explore the ways in which exercise can improve your eye health and how it can play a crucial role in preserving your vision for the long term.
1. Improved Blood Circulation and Oxygen Supply
One of the primary ways exercise benefits eye health is by improving blood circulation throughout the body, including the eyes. The eyes are highly sensitive organs, requiring a consistent supply of oxygen and nutrients to function properly. When we engage in physical activity, our heart rate increases, and blood flow is enhanced, ensuring that the eyes receive an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients.
- Impact on Vision: Proper blood flow helps to maintain the health of the retina, the part of the eye responsible for processing light and transmitting signals to the brain. Enhanced circulation can reduce the risk of retinal diseases and support the repair of any damage caused by oxidative stress.
- Examples of Exercise: Aerobic exercises such as walking, jogging, cycling, and swimming are especially beneficial for improving blood flow to the eyes. Engaging in these activities regularly can help ensure that your eyes are receiving the nutrients they need to stay healthy.
2. Reduced Risk of Eye Diseases Associated with Aging
As we age, the risk of developing certain eye conditions, such as glaucoma, macular degeneration, and cataracts, increases. However, studies suggest that regular exercise can help reduce the risk of these age-related conditions by improving overall health and maintaining a healthy weight.
- Glaucoma: This condition involves increased pressure within the eye, which can damage the optic nerve and lead to vision loss. Regular exercise has been shown to help lower intraocular pressure, which is a key factor in managing and preventing glaucoma.
- Macular Degeneration: This leading cause of vision loss in older adults is linked to the deterioration of the macula, the part of the retina responsible for central vision. Research suggests that regular physical activity can improve the health of the retina and may reduce the progression of age-related macular degeneration.
- Cataracts: Cataracts, which cause clouding of the lens, are often a result of aging, but exercise can help reduce the oxidative stress that contributes to cataract formation. Additionally, regular activity can improve blood flow, preventing the lens from deteriorating prematurely.
By maintaining a healthy lifestyle through exercise, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing these age-related eye conditions.
3. Enhanced Eye Coordination and Focus
Exercise can also improve the coordination between the eyes and the brain, leading to better visual processing and focus. This is particularly important for individuals who engage in activities requiring fine motor skills or precise vision, such as reading, driving, or sports.
- Visual Skills: Activities that require quick shifts in focus or movement, such as sports or certain types of workouts, can help enhance eye tracking, coordination, and reaction time. For example, tennis, basketball, and swimming all require fast visual processing to track moving objects or navigate the environment.
- Eye Muscle Strength: Physical exercise can also strengthen the muscles that control eye movement, helping to maintain proper alignment and reducing the risk of conditions such as strabismus (crossed eyes) or eye fatigue. Stronger eye muscles can contribute to clearer vision, especially when performing tasks that involve prolonged visual focus.
Exercise helps ensure that both the eyes and the brain work in harmony, which is vital for maintaining healthy and efficient vision.
4. Stress Reduction and Its Impact on Eye Health
Stress is often linked to a variety of health issues, including eye conditions. For example, stress can exacerbate dry eye syndrome, increase the risk of developing eye infections, and even lead to vision problems caused by eye strain. Regular exercise is an effective way to reduce stress and its negative effects on the eyes.
- Cortisol and Eye Health: When we are stressed, our bodies produce more cortisol, a hormone that can affect the immune system and increase inflammation. Chronic stress can lead to conditions such as dry eye, eye irritation, and even increased intraocular pressure, which contributes to glaucoma.
- Exercise as Stress Relief: Physical activity helps lower cortisol levels, reduce anxiety, and promote the release of endorphins, which are natural mood boosters. By engaging in regular exercise, individuals can alleviate stress, improving both their mental and eye health.
Taking time for physical activity can significantly reduce the physical and emotional stress that negatively impacts vision.
5. Prevention of Obesity-Related Vision Issues
Obesity is a known risk factor for a variety of chronic conditions, including diabetes, high blood pressure, and cardiovascular disease. These conditions, in turn, can have serious consequences for eye health, leading to conditions such as diabetic retinopathy, hypertensive retinopathy, and even vision loss.
- Diabetic Retinopathy: Diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels in the retina, leading to vision impairment. Exercise helps regulate blood sugar levels and prevent or manage type 2 diabetes, which can reduce the risk of developing diabetic retinopathy.
- Hypertension and Eye Health: High blood pressure can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to conditions such as retinopathy or even blindness. Regular exercise is essential in managing blood pressure, helping to protect the eyes from the adverse effects of hypertension.
By maintaining a healthy weight and exercising regularly, individuals can reduce their risk of obesity-related conditions that can compromise eye health.
6. Improving Sleep and Its Effect on Eye Health
Sleep is essential for overall health, including the health of your eyes. During sleep, the body repairs itself, and the eyes undergo necessary restorative processes. However, inadequate sleep can lead to a variety of eye-related issues, such as dry eyes, eye strain, and even blurred vision.
- Exercise and Sleep Quality: Regular physical activity promotes better sleep by helping to regulate the body’s sleep-wake cycle. It also reduces symptoms of insomnia, allowing for deeper, more restorative sleep.
- Impact on Eye Health: Better sleep contributes to the repair and rejuvenation of the eyes, reducing the risk of eye fatigue, dryness, and strain. Additionally, quality sleep is vital for the proper function of the optic nerve and other parts of the visual system.
Incorporating exercise into your daily routine can significantly improve sleep quality, which in turn supports eye health.
Conclusion
Exercise is not only beneficial for physical and mental well-being but also plays a critical role in maintaining optimal eye health. By improving blood circulation, reducing the risk of age-related eye conditions, enhancing eye coordination, alleviating stress, and preventing obesity-related complications, regular physical activity is a powerful tool in preserving vision. Incorporating simple exercises into your daily routine, such as aerobic activities, strength training, and even stretching, can have a lasting positive impact on your eye health. By making exercise a priority, you are investing in your long-term vision and quality of life.

 Top 5 Benefits of Specialized Healthcare for Veterans
Top 5 Benefits of Specialized Healthcare for Veterans  Which delta 9 gummies are known for their potency?
Which delta 9 gummies are known for their potency?  Ways to Relieve Back Pain Naturally
Ways to Relieve Back Pain Naturally 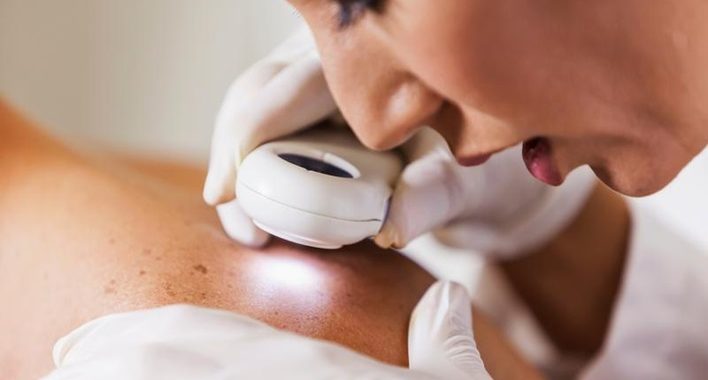 The Life-Saving Benefits of Mohs Surgery for Skin Cancer
The Life-Saving Benefits of Mohs Surgery for Skin Cancer  Finding the Right Florida Pain Management Center
Finding the Right Florida Pain Management Center  A Lifetime of Brain Health: Tips for Every Decade
A Lifetime of Brain Health: Tips for Every Decade  From Breath to Flow: Understanding the Role of Pranayama in Vinyasa Yoga
From Breath to Flow: Understanding the Role of Pranayama in Vinyasa Yoga  The Role of Supplements in Modern Health: A Balanced Perspective
The Role of Supplements in Modern Health: A Balanced Perspective